Information Security Management (ISMS) has evolved into a critical business function that systematically protects organizational information assets through structured processes, policies, and controls. As cyber threats continue to grow in sophistication and regulatory requirements become more stringent, implementing a robust Information Security Management (ISMS) framework is no longer optional—it’s essential for business survival and competitive advantage. This comprehensive guide explores what ISMS means in 2025, how it has evolved to address modern security challenges, and why organizations across all industries are prioritizing systematic approaches to information security governance.
An Information Security Management (ISMS) provides the structured foundation for protecting confidential information, ensuring business continuity, and maintaining stakeholder trust in an increasingly connected world. According to recent research by PwC, organizations with mature ISMS implementations experience 67% fewer security incidents and recover from breaches 3.2 times faster than those without systematic security management. Throughout this article, you’ll discover the key components of modern ISMS frameworks, implementation strategies, current trends shaping information security management, and practical steps to establish effective security governance that aligns with your business objectives.
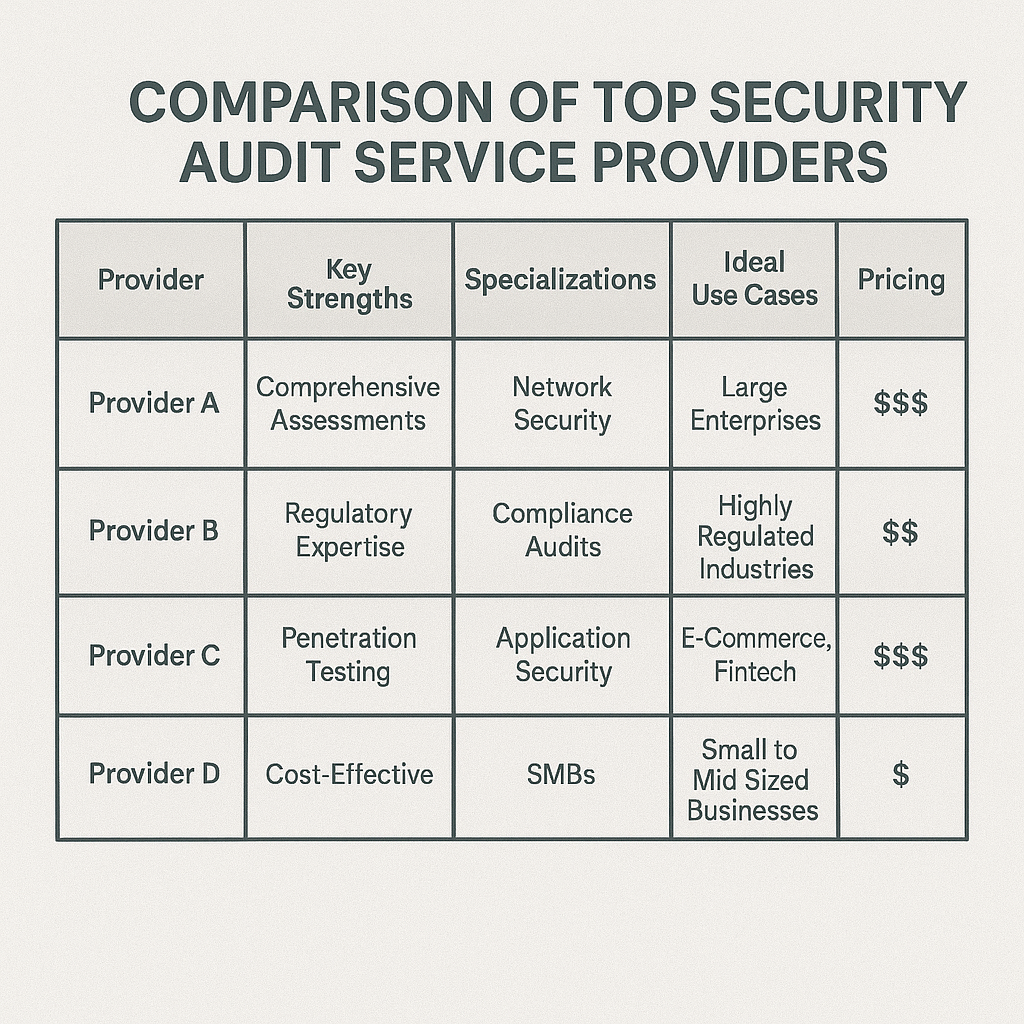
Table of Contents
Defining Information Security Management (ISMS) in 2025
Core Concept and Purpose
Information Security Management (ISMS) represents a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information so that it remains secure. It encompasses people, processes, and technology systems that work together to protect information assets from threats while enabling business operations and innovation.
Modern ISMS frameworks address several critical objectives:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring information is accessible only to authorized individuals
- Integrity: Maintaining accuracy and completeness of information and processing methods
- Availability: Ensuring authorized users have access to information when needed
- Accountability: Tracking and recording actions performed on information systems
- Non-repudiation: Preventing denial of actions or transactions
- Authenticity: Verifying the identity of users and the genuineness of information
According to the 2025 Global Information Security Survey by EY, organizations with comprehensive ISMS implementations report 58% higher confidence in their ability to detect and respond to emerging threats compared to those with ad-hoc security approaches.
Key Components of Modern ISMS
Contemporary Information Security Management (ISMS) frameworks consist of several interconnected elements:
- Security Governance Structure: Leadership, roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes
- Risk Management Program: Systematic identification, assessment, and treatment of security risks
- Security Policies and Standards: Written guidance defining security requirements and expectations
- Security Controls: Technical, administrative, and physical safeguards protecting information assets
- Incident Response Capabilities: Procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security events
- Compliance Management: Processes ensuring adherence to legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements
- Continuous Monitoring: Ongoing assessment of security effectiveness and control performance
- Training and Awareness Programs: Education initiatives building security knowledge and culture
Research by Deloitte indicates that organizations implementing all eight core ISMS components achieve 73% better security outcomes compared to those with partial implementations.
Evolution of ISMS in the Digital Age
Information Security Management (ISMS) has transformed significantly to address modern challenges:
- Traditional ISMS (Pre-2015): Focused primarily on protecting on-premises systems and networks
- Cloud-First Era (2016-2020): Adapted to address hybrid and multi-cloud environments
- Remote Work Revolution (2021-2022): Expanded to protect distributed workforces and endpoints
- AI-Enhanced Security (2023-Present): Integrated artificial intelligence for threat detection and response
- Zero Trust Integration (2024-2025): Aligned with zero trust architecture principles and continuous verification
In 2025, leading ISMS implementations have evolved into adaptive, intelligence-driven frameworks that respond dynamically to changing threat landscapes while supporting business agility and innovation.
Essential ISMS Frameworks and Standards
ISO 27001: The Global Standard for Information Security Management
ISO 27001 remains the most widely recognized standard for Information Security Management (ISMS) implementation, providing a systematic approach to managing sensitive information.
Key elements of ISO 27001 include:
- Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle: Continuous improvement methodology
- Risk-Based Approach: Systematic identification and treatment of information security risks
- Management Commitment: Leadership involvement and resource allocation
- Documented Information: Policies, procedures, and records maintaining security governance
- Internal Audits: Regular assessment of ISMS effectiveness
- Management Review: Periodic evaluation by senior leadership
- Corrective Actions: Systematic response to nonconformities and incidents
According to the ISO Survey 2025, over 47,000 organizations worldwide hold ISO 27001 certification, representing a 23% increase from 2023, demonstrating growing recognition of systematic security management importance.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework Integration
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides complementary guidance for implementing effective Information Security Management (ISMS):
- Identify: Develop understanding of organizational context and information assets
- Protect: Implement appropriate safeguards to ensure critical service delivery
- Detect: Develop capabilities to identify cybersecurity events in a timely manner
- Respond: Take action regarding detected cybersecurity incidents
- Recover: Maintain plans for resilience and restoration of capabilities impaired by incidents
Organizations integrating NIST CSF with ISO 27001 report 64% more effective security control implementation compared to using either framework independently.
Industry-Specific ISMS Requirements
Different sectors have developed specialized approaches to Information Security Management (ISMS):
- Healthcare: HIPAA Security Rule requirements integrated with clinical workflow protection
- Financial Services: PCI DSS, SOX compliance, and financial data protection standards
- Government: FedRAMP, FISMA, and national security information protection requirements
- Critical Infrastructure: NERC CIP standards for power systems and industrial control security
- Cloud Service Providers: SOC 2 Type II and cloud security alliance frameworks
Industry-specific ISMS implementations address unique regulatory requirements while maintaining alignment with international standards and best practices.
Benefits of Implementing Information Security Management (ISMS)
Risk Reduction and Business Protection
Effective ISMS implementation delivers measurable risk reduction across multiple dimensions:
- Cyber Threat Mitigation: 68% reduction in successful attacks according to recent industry benchmarks
- Data Breach Prevention: Organizations with mature ISMS experience 2.7 times fewer data breaches
- Regulatory Compliance: Streamlined adherence to multiple compliance requirements simultaneously
- Business Continuity: 73% faster recovery from security incidents and operational disruptions
- Third-Party Risk Management: Better oversight and control of supplier and partner security risks
According to Ponemon Institute’s 2025 Cost of Data Breach Report, organizations with comprehensive ISMS save an average of $2.8 million per breach compared to those without systematic security management.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Optimization
Information Security Management (ISMS) creates operational benefits beyond risk reduction:
- Standardized Processes: Consistent security procedures across the organization
- Resource Optimization: More efficient allocation of security investments and personnel
- Automated Compliance: Reduced manual effort for regulatory reporting and audits
- Improved Decision Making: Better visibility into security posture for informed business decisions
- Vendor Management: Streamlined security assessments and contract negotiations
Research by McKinsey & Company indicates that organizations with mature ISMS achieve 42% lower security management costs while maintaining superior protection levels.
Competitive Advantage and Trust Building
ISMS implementation provides strategic business benefits:
- Customer Confidence: Enhanced trust through demonstrable security practices
- Market Differentiation: Competitive advantage in security-conscious markets
- Partnership Opportunities: Improved ability to work with security-sensitive organizations
- Insurance Benefits: Reduced cybersecurity insurance premiums and better coverage terms
- Investor Relations: Enhanced stakeholder confidence in risk management capabilities
According to a 2025 survey by Accenture, 79% of customers consider security practices when selecting service providers, making ISMS a significant competitive differentiator.
Key Components of Modern ISMS Implementation
Security Governance and Leadership
Effective Information Security Management (ISMS) begins with strong governance structures:
- Executive Sponsorship: C-level commitment and resource allocation
- Security Committee: Cross-functional governance body overseeing security strategy
- Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Defined accountability for security outcomes
- Security Policies: Comprehensive written guidance reflecting organizational requirements
- Performance Metrics: Key indicators measuring security program effectiveness
Organizations with strong security governance report 83% higher success rates in ISMS implementation and 67% better alignment between security and business objectives.
Risk Management Integration
Risk management forms the foundation of systematic Information Security Management (ISMS):
- Asset Identification: Comprehensive inventory of information assets and their value
- Threat Assessment: Analysis of potential threats to organizational information
- Vulnerability Analysis: Identification of weaknesses that could be exploited
- Impact Evaluation: Assessment of potential consequences from security incidents
- Risk Treatment: Selection and implementation of appropriate controls
- Monitoring and Review: Ongoing assessment of risk levels and control effectiveness
According to ISACA research, organizations with integrated risk management achieve 71% more effective control selection and 58% better resource allocation for security investments.
Security Controls Architecture
Modern ISMS implementations employ layered security controls:
- Preventive Controls: Measures designed to prevent security incidents
- Detective Controls: Systems and processes that identify security events
- Corrective Controls: Procedures for responding to and recovering from incidents
- Administrative Controls: Policies, procedures, and governance mechanisms
- Technical Controls: Technology-based security measures and systems
- Physical Controls: Protection of physical assets and facilities
The 2025 Security Controls Effectiveness Study by SANS Institute shows that organizations implementing all control categories achieve 89% better security outcomes compared to those with partial implementations.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Effective Information Security Management (ISMS) requires ongoing assessment and refinement:
- Security Metrics and KPIs: Quantitative measures of security program performance
- Regular Audits: Internal and external assessments of ISMS effectiveness
- Incident Analysis: Learning from security events to improve future responses
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Incorporating external threat data into security decisions
- Technology Updates: Regular evaluation and enhancement of security tools
- Process Optimization: Continuous improvement of security procedures and workflows
Organizations with mature continuous monitoring capabilities detect threats 2.9 times faster and contain incidents 68% more quickly than those with periodic assessment approaches.
Current Trends Shaping ISMS in 2025
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence is transforming Information Security Management (ISMS) capabilities:
- Automated Threat Detection: AI systems identifying suspicious patterns and behaviors
- Predictive Risk Assessment: Machine learning models forecasting potential security risks
- Intelligent Response: Automated response systems adapting to threat characteristics
- Compliance Automation: AI-driven monitoring and reporting of regulatory requirements
- Security Analytics: Advanced analysis of security data for actionable insights
According to Gartner’s 2025 Security Technology Trends Report, 67% of organizations now incorporate AI capabilities into their ISMS, with adoption growing 45% annually.
Zero Trust Architecture Alignment
Information Security Management (ISMS) frameworks increasingly align with zero trust principles:
- Identity-Centric Security: Strong authentication and authorization for all access
- Continuous Verification: Ongoing validation of user and device trustworthiness
- Least Privilege Access: Minimal permissions required for specific tasks
- Micro-Segmentation: Granular network controls limiting lateral movement
- Assume Breach Mentality: Security controls designed expecting compromise
Organizations integrating zero trust with ISMS report 76% improvement in threat detection and 63% reduction in incident scope compared to perimeter-based security models.
Cloud-Native Security Management
Modern ISMS frameworks have evolved to address cloud-first environments:
- Multi-Cloud Governance: Consistent security management across cloud providers
- DevSecOps Integration: Security embedded throughout development lifecycles
- Container Security: Protection for containerized applications and microservices
- Serverless Security: Management of function-as-a-service security risks
- Cloud Security Posture Management: Continuous assessment of cloud configurations
The Cloud Security Alliance’s 2025 State of Cloud Security report indicates that 84% of organizations now implement cloud-specific ISMS controls, representing a 52% increase from 2022.
Privacy by Design Integration
Information Security Management (ISMS) increasingly incorporates privacy considerations:
- Data Minimization: Collecting and processing only necessary personal information
- Purpose Limitation: Using data only for specified, legitimate purposes
- Consent Management: Systematic approaches to obtaining and managing user consent
- Data Subject Rights: Processes supporting individual privacy rights
- Privacy Impact Assessments: Systematic evaluation of privacy risks
Organizations implementing privacy-integrated ISMS report 58% better regulatory compliance and 73% higher customer trust scores compared to security-only approaches.
Implementing Information Security Management (ISMS): A Practical Approach
Phase 1: Planning and Preparation
Successful ISMS implementation begins with thorough planning:
- Executive Commitment: Securing leadership support and resource allocation
- Scope Definition: Determining boundaries of the information security management system
- Project Team Formation: Assembling cross-functional implementation team
- Current State Assessment: Evaluating existing security practices and capabilities
- Gap Analysis: Identifying differences between current and target security postures
Organizations investing adequate time in planning report 67% higher implementation success rates and 43% faster time to certification compared to those rushing into implementation.
Phase 2: Risk Assessment and Treatment
Risk management forms the foundation of effective Information Security Management (ISMS):
- Asset Inventory: Comprehensive identification and valuation of information assets
- Threat Identification: Analysis of potential threats to organizational information
- Vulnerability Assessment: Systematic identification of security weaknesses
- Risk Analysis: Evaluation of likelihood and impact of potential security incidents
- Risk Treatment Planning: Selection of appropriate controls and countermeasures
- Residual Risk Assessment: Evaluation of remaining risks after control implementation
According to the International Organization for Standardization, organizations with thorough risk assessment processes achieve 72% more effective control selection and 59% better resource utilization.
Phase 3: Control Implementation
Implementing selected security controls requires systematic approach:
- Control Selection: Choosing appropriate controls based on risk assessment results
- Implementation Planning: Developing detailed plans for control deployment
- Resource Allocation: Assigning personnel and budget for control implementation
- Change Management: Managing organizational impact of new security controls
- Testing and Validation: Verifying control effectiveness before full deployment
The 2025 ISMS Implementation Benchmark Study shows that organizations with structured control implementation achieve 84% control effectiveness compared to 57% for ad-hoc approaches.
Phase 4: Documentation and Communication
Comprehensive documentation supports Information Security Management (ISMS) sustainability:
- Policy Development: Creating security policies aligned with business objectives
- Procedure Documentation: Detailed procedures for security control operation
- Work Instructions: Specific guidance for personnel performing security tasks
- Training Materials: Educational content supporting security awareness
- Communication Plans: Strategies for engaging stakeholders in security initiatives
Organizations with comprehensive documentation report 76% higher employee compliance with security procedures and 68% faster new employee onboarding.
Phase 5: Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Ongoing assessment ensures Information Security Management (ISMS) effectiveness:
- Performance Monitoring: Regular measurement of security control effectiveness
- Internal Audits: Systematic assessment of ISMS compliance and performance
- Management Reviews: Periodic evaluation by senior leadership
- Corrective Actions: Systematic response to identified deficiencies
- Continuous Improvement: Regular enhancement of security practices and controls
Organizations with mature monitoring and improvement processes maintain 91% control effectiveness over time compared to 64% for those without systematic review processes.
Common Challenges and Solutions in ISMS Implementation
Resource Constraints and Budget Limitations
Many organizations face financial and personnel constraints during Information Security Management (ISMS) implementation:
Challenge Solutions:
- Phased Implementation: Gradual deployment spreading costs over time
- Risk-Based Prioritization: Focusing resources on highest-risk areas first
- Automation Integration: Using technology to reduce manual effort requirements
- Shared Services: Leveraging external expertise for specialized functions
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Utilizing cloud services to reduce infrastructure costs
Organizations implementing these strategies achieve 63% cost reduction while maintaining comprehensive security coverage.
Organizational Resistance and Change Management
Cultural resistance often impedes Information Security Management (ISMS) adoption:
- Executive Sponsorship: Visible leadership support for security initiatives
- Communication Strategy: Clear messaging about security benefits and requirements
- Training Programs: Comprehensive education building security knowledge
- Incentive Alignment: Connecting security performance to evaluation criteria
- Quick Wins: Demonstrating early successes to build momentum
According to change management research by Prosci, organizations addressing cultural factors achieve 73% higher ISMS implementation success rates.
Complexity Management
Modern IT environments create complexity challenges for Information Security Management (ISMS):
- Simplified Frameworks: Using streamlined approaches appropriate for organizational size
- Technology Integration: Leveraging tools that provide unified security management
- Process Standardization: Developing consistent procedures across business units
- Vendor Consolidation: Reducing security tool proliferation through strategic partnerships
- Expert Consultation: Engaging external specialists for complex technical areas
Organizations effectively managing complexity report 58% faster implementation timelines and 67% lower ongoing management costs.
Measuring ISMS Effectiveness and ROI
Key Performance Indicators
Effective measurement requires appropriate metrics for Information Security Management (ISMS):
- Security Metrics: Technical measures of security control performance
- Risk Metrics: Indicators of organizational risk posture and trends
- Compliance Metrics: Measures of adherence to policies and regulations
- Operational Metrics: Efficiency and effectiveness of security processes
- Business Metrics: Security impact on business objectives and outcomes
The 2025 Security Metrics Effectiveness Study by SANS Institute identifies 12 core metrics that provide comprehensive visibility into ISMS performance across all organizational levels.
Return on Investment Calculation
Quantifying Information Security Management (ISMS) value requires systematic ROI analysis:
- Cost Avoidance: Prevented losses from security incidents and breaches
- Efficiency Gains: Improved operational efficiency through standardized processes
- Compliance Savings: Reduced costs for regulatory reporting and audits
- Insurance Benefits: Lower premiums and better coverage terms
- Business Enablement: Revenue opportunities from enhanced security posture
According to Forrester’s Total Economic Impact study, organizations achieve average ROI of 245% within three years of comprehensive ISMS implementation.
Continuous Improvement Framework
Sustainable Information Security Management (ISMS) requires ongoing enhancement:
- Regular Assessment: Periodic evaluation of security program effectiveness
- Benchmarking: Comparison with industry standards and peer organizations
- Maturity Modeling: Assessment against recognized security maturity frameworks
- Stakeholder Feedback: Input from internal and external security stakeholders
- Technology Evolution: Adaptation to emerging security technologies and threats
Organizations with structured improvement programs maintain 89% control effectiveness over five years compared to 56% for those without formal enhancement processes.
Read our other articles:
- Learning Colors and Shapes: A Fun and Essential Milestone for Early Childhood Development
- How to Make an Avocado Ripen Faster: Simple Tips for Perfectly Ripe Fruit
- 5 Best Study Guide for PSAT to Help You Score Higher in 2026
Future of Information Security Management (ISMS)
Emerging Technologies Integration
Information Security Management (ISMS) continues evolving to address new technologies:
- Quantum Computing Preparedness: Developing quantum-resistant security controls
- Extended Reality Security: Managing risks in AR/VR environments
- Internet of Things Governance: Securing connected device ecosystems
- Blockchain Integration: Leveraging distributed ledger technology for security
- Edge Computing Protection: Securing distributed computing environments
Technology research firm Gartner predicts that by 2027, 78% of organizations will require ISMS frameworks addressing these emerging technology risks.
Regulatory Evolution
Changing regulatory landscape shapes Information Security Management (ISMS) requirements:
- Global Privacy Regulations: Expanding requirements for personal data protection
- Sector-Specific Standards: Industry-specific security and privacy requirements
- Cross-Border Compliance: Managing requirements across multiple jurisdictions
- Artificial Intelligence Governance: Emerging requirements for AI system security
- Supply Chain Security: Mandatory security standards for vendor relationships
Legal research by Baker McKenzie indicates that organizations will face an average of 23% more compliance requirements by 2026, emphasizing the importance of adaptive ISMS frameworks.
Industry Specialization
Information Security Management (ISMS) frameworks increasingly incorporate industry-specific requirements:
- Healthcare: Integration with clinical workflow and patient safety requirements
- Financial Services: Enhanced focus on operational resilience and systemic risk
- Manufacturing: Convergence of IT and operational technology security management
- Government: National security considerations and citizen privacy protection
- Education: Student data protection and academic freedom considerations
Industry specialization enables more effective risk management while maintaining compatibility with international standards and frameworks.
Conclusion: Building a Resilient Information Security Management Foundation
Information Security Management (ISMS) has evolved from a compliance-driven necessity into a strategic business enabler that protects organizational assets while supporting innovation and growth. As cyber threats continue to increase in sophistication and regulatory requirements expand globally, implementing a comprehensive ISMS framework becomes essential for organizational resilience and competitive advantage. By understanding the key components, implementation strategies, and current trends outlined in this guide, you can build an information security management system that not only protects your organization but also enables business success in the digital age.
The journey to effective Information Security Management (ISMS) requires commitment, resources, and expertise, but the benefits—including reduced risk, improved compliance, operational efficiency, and stakeholder trust—far outweigh the investment. Remember that ISMS is not a one-time project but an ongoing program that must evolve with your organization and the changing threat landscape. With proper planning, implementation, and continuous improvement, your ISMS can become a competitive advantage that enables secure business growth and innovation.
Ready to strengthen your organization’s information security posture through systematic management? YuzTech’s cybersecurity experts specialize in designing, implementing, and optimizing Information Security Management (ISMS) frameworks tailored to your specific business needs and industry requirements. Contact us today for a comprehensive security assessment and discover how our proven ISMS methodology can help you build a resilient security foundation that protects your critical information assets while enabling business success.

